Ex-ante assessment of options
According to the light design method, the different options were assessed using the grid described elsewhere in the course (here).
Case study | Assessment grid | Strengths and Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
San Giuliano (E6) | Strength of these options is the complementarity between them: both options enhance the soil fertility and allow farmers to reduce crop inputs. This is why agronomy and autonomy increased compared to reference situation. Furthermore, options fit the local challenges and civil society attempts towards agriculture (social embeddedness is improved compared to reference situation). | |
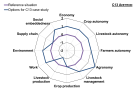
Aveyron (C13) | Strengths of options are numerous:
Weaknesses are related to (i) the decrease of crop production so the territory cannot supply another one, (ii) the decrease of meat and milk production, and more local markets, that impacts supply chain activities, and (iii) the increase of management complexity in diversified systems. | |
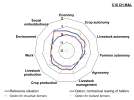
CH M&L (C18) | For the mountain farmers, main advantages of such a system based on contractual rearing of heifers are:
For the lowland farmers, main advantages of such a system based on contractual rearing of heifers are:
The main disadvantage is that such long-distance partnership between farmers are very challenging. |